Confounding variables are the 3rd alternative in a study searching for eventual cause-and-effect interrelations. It is associated with both the exposure and the outcome without being on the causal pathway between the two.

What Are Confounding Variables Effects And Controlling Analytics Steps
Types of Confounding Variables.

. In case-control and cohort studies confounding may have any one of the following effects. Potential confounding variables may explain the differences between groups rather than the treatment variable. Observational studies are not scientific in nature.
Which of the following is NOT a criteria for confounding. These include the following. 3 Interactions between the experimenter and participants.
Confounding is defined in terms of the data generating model as in the figure above. Confounding Variables Internal Validity. Factor Z may be a _____ CONFOUNDER.
Failing to account for confounders may distort the values and thus lead to inaccurate study results. 1 it must have an association with the disease that is it should be a risk factor for the disease. This paper explains that to be a potential confounder a variable needs to satisfy all three of the following criteria.
A Confounder is an extraneous variable whose presence affects the variables being studied so that the results do not reflect the actual relationship between the variables under study. And 3 it must not be an effect of the exposure. A confounding variable is independently associated with both the risk factor exposure and the disease outcome.
Such factors are related to supposed reason and have an influence on a dependent variable. Factor is a risk factor for the outcome. O Handedness whether you write with your left or right hand.
Observational studies often do not involve a large enough sample to draw cause-and-effect conclusions. A type of extraneous variable that systematically affects one or more levels of the IV differently. While increased exercise may lead to reduced blood pressure an individuals starting weight also has a big impact on the relationship between these two variables.
2 it must be associated with the exposure that is it must be unequally distributed between exposure groups. Because of the dual association the confounding variable creates a false association between the risk factor and disease or can exaggerate or hide a true association. Confounding must always be considered as a possible explanation for a perceived exposure-outcome relationship.
One potential confounding variable is starting weight which is correlated with exercise and has a direct causal effect on blood pressure. Also known as confounding factors confounding variables are a type of extraneous variable linked with both the dependent and independent variables of the study. The amount of association above and beyond that which can be explained by confounding factors provides a more appropriate estimate of the true association which is due to the exposure.
It has been proven so in previous studies. Researchers may be biased in the observations they choose to record. The definition of confounding variable.
Previous experience because each persons behaviour is measured more than once. A variable is a confounder if it satisfies one of the following conditions. -Arise from researchers knowledge of the hypothesis the nature if the experimental.
Adjusting for it produces more than 10 change in the relationship between the exposure and the outcome. Confounding variables or confounders are often defined as the variables correlate positively or negatively with both the dependent variable and the independent variable. For a variable to qualify as a confounding variable it must meet two criteria.
Restriction - restrict based on confounding variable if sex is confounding variable restrict to females only Matching - match on the confounding variable if sex is confounding variable match on sex. Each person is unique so they will behave differently. Experimental designs are more powerful than.
Let X be some independent variable and Y some dependent variableTo estimate the effect of X on Y the statistician must suppress the effects of extraneous variables that influence both X and YWe say that X and Y are confounded by some other variable Z whenever Z causally influences both X. Confounding variables are those that may compete with the exposure of interest eg treatment in explaining the outcome of a study. Which of the following variables may be a confounding variable in a within-subjects design.
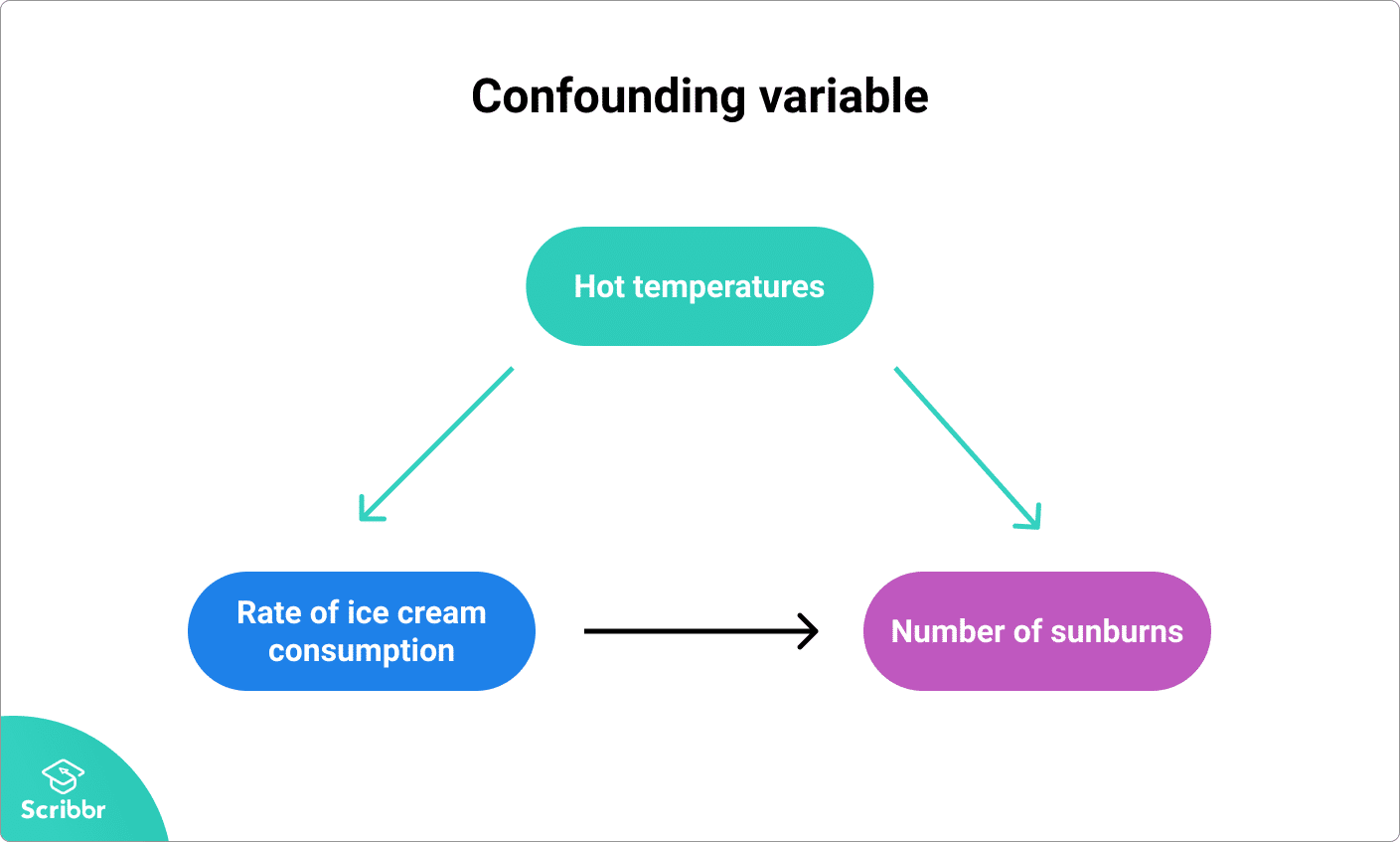
Confounding Variables Definition Examples And Controls

0 Comments